Glove Materials
Natural Materials
Bamboo
Bamboo is natural fibre made from an herbaceous plant. It’s very soft, velvety and slightly glossy. Bamboo fibre has anti-microbial and anti-fungal properties that are retained even after numerous washings. These anti-microbial properties reduce or remove the unpleasant odours that can develop when wearing other gloves. Bamboo is an ecologically sound crop; since no pesticides are used in its cultivation. Bamboo fibre can absorb moisture 3-4 times faster than cotton and dries twice as fast. This amazing natural fibre is non-irritant to the skin so Bamboo gloves are an essential alternative for people who suffer from allergies and sensitive skin conditions.

Cotton
Cotton (CO) is a plant that is usually processed ito yarn, suitable for soft, air permeable textile production. Woven or knitted cotton textile features great moisture absorption and is easy to wash. It does not acquire electric charge and maintains its features up until 150°C. Because of this, it is perfectly suitable for clothing that is in direct contact with the skin. The recommended washing temperature of cotton textile is up to 60°C. Cotton is often mixed with different synthetic yarns, especially polyester and polyamide, which ensure durability and longevity of the fabric. The cotton fibre is not elastic, thus it is often also mixed with elastane.
Latex
Latex is an elastic and highly durable material that is made from rubber tree sap. Rubber is elastic because of its macromolecules forming spirals. The molecules elongate when stretched and coil back into spirals when released. This specific feature enables latex to adapt naturally to different hand shapes. It is very elastic (elongation limit 750 %) and has a long life span. Latex provides good protection against the majority of alkaline solutions and detergents. Latex is very durable and tear resistant but it can be punctured easily with sharp objects. The major drawback of latex is its composition that includes proteins and chemical allergens, and thus may induce an allergic response in some individuals.
Leather
Leather is durable, pliable, supple and has exceptional breathability properties. Furthermore, it has the ability to absorb moisture, which means a leather glove rarely feels moist, but is instead perceived as dry and comfortable.
To soften the leather, Chromium (VI) is added during the tanning process. This can cause allergic reactions in certain individuals. An upper limit is therefore specified for Chromium (VI) content in leather gloves. EN 420 specifies this limit as max. 3 mg/kg Chromium (VI).
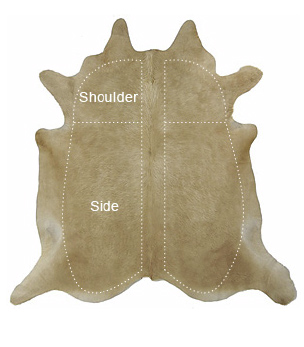
Split and Grain Leather – What's the Difference?
The properties of hide vary, depending on which part of the animal the hide comes from. Hide from the sides forms Split Leather, which has the highest durability. Hide from the shoulders on the other hand, although still very strong, is less durable than side split leather, forming Grain Leather.
Grain/nappa Leather Grain/nappa leather is made from the smooth surface of the hide and is durable, supple, sensitive and moisture absorbing. It is therefore an excellent choice for uses where the requirements for dexterity are high, e.g. assembly gloves.
Split/suede Leather Split/suede leather has a rougher surface than grain leather. It comes in a number of thicknesses and is heat resistant. For this reason, split leather is highly suitable for work gloves designed for rough handling, or for welding gloves, which must withstand high temperatures and sparks.

Goatskin This leather features detailed and embossed grain appearance, i.e. beautiful natural leather surface patterns. Goatskin is distinguished by its suppleness, low thickness and relatively high durability. The grain layer of some leather types, including goat, is slightly polished and achieves a beautiful appearance while being light-weight and elastic.

Pig grain Pig grain is leather differing from the other types. Its grain layer features creasing, random and relatively large bristle pores as well as a slightly rougher general grain pattern. Bristles start growing in relatively deep skin layers beneath the hide, therefore pig grain has many little channels throughout its surface which increase water permeability of the membrane and cause some maceration. The leather thickness is generally slightly uneven. This leather characteristically has low wear, relatively high durability but low elasticity.

Cow grain Cow grain leather features good appearance, suppleness, tender and even surface, a fine grain pattern and relatively even thickness throughout the whole surface. Cow grain leather is very strong. The cow leather differs from the calf leather by its grain pattern, which is slightly rougher, greater thickness and increased rigidity. Cow grain features low water permeability and maceration compared to pig grain.

Cow split Cow split is leather with a fluffy surface. The fluffiness is achieved by polishing of the inner surface. Due to this polishing the cow split leather is less durable than the cow grain leather, however cow split leather features excellent consistency in thickness throughout the whole surface. Cow split leather is soft, supple and tender and it has favourable physical and mechanical properties. The cow split surface has small funnel-like bristle pores that are almost invisible as they are covered by longer fuzz. Cow split leather features significantly lower water permeability and maceration when compared to pig grain.
Synthetic Materials
Acrylic fibre
Acrylic fibre is synthetic fibre that contains at least 85% of acrylonitrile. It is characterised by flexibility, resistance to moths, petrol and chemical products, as well as direct sunlight. Acrylic fibre is usually used for knitted textile, e.g. fleece wear, sports and children garments.
Cordura®
Cordura® is a long-lasting, very solid and abrasion resistant material. It is polyamide fabric with durable polyurethane coating that is treated with water resistant TEFLON® coating. Cordura® is a patented trademark of DuPont™ used for any durable material of this category irrespective of thickness. The Cordura® material is stain resistant, fairly easy to clean and has an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
Elastane
Elastane (EL) is synthetic elastomeric fibre consisting of at least 85% polyurethane. It is elastic, and even when stretched to three times its initial length, the fabric will immediately return to its original form as soon as the tensile force is eliminated. The monofilament or multifilament yarns of this fibre are used as components for different fibre compositions. Yarns with elastane ensure high elasticity of polyester, nylon, cotton or other joint composition materials, and the clothing made with these fabrics ensure that they provide a comfortable and snug fit around the body.
EVA
EVA is ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer. It contains small amounts of vinyl acetate (up to 6%). EVA is attributed to high pressure polyethylene group materials. If it contains a higher percentage of vinyl acetate, the material elasticity is proportionally increased. This material is highly water and gas resistant.
Kevlar®
Kevlar® is para-aramid fibre that is highly durable, flexible and relatively light-weight. Kevlar® tensile resistance is five times higher when compared to steel, and it is heat resistant even up to 370°C. This fibre is non-flammable and extremely cut resistant. The yarn that is made of this fibre is suitable both for woven and knitted fabric productions, technical textile, and widely used for production of bulletproof vests, military or firefighter clothing and cut resistant gloves. Usually the yarn of Kevlar® fibre is used for sewing of heat resistant gloves.
Kozane®
Kozane® is an innovative range of high performance fabrics, with high cut, abrasion and puncture resistance, yet soft and flexible. Mainly used for manufacturing protective clothing and gloves, the Kozane® range protects the wearer against cuts and lacerations.
KR-Grip®
KR-Grip® is a fabric that offers strong grip. The special surface structure formed of PVC enables expulsion of moisture when working in wet conditions, and guarantees good fabric flexibility. The core of KR-Grip® is strong, soft and wrinkle resistant knitted fabric from polyester and cotton.
Lycra®
Lycra® is the trademark of DuPont™ and it describes elastane (EL) without latex or natural rubber (e.g. elastane of other trademarks may contain some percent of latex).
MacroSkin Pro®
MacroSkin Pro® is a mechanically strong and very elastic material. It is also soft and thin, while its surface is quite smooth and, therefore, pleasant to touch. The fabric structure consists of the combination of nylon and polyester, which improves abrasion resistance, guarantees wrinkle resistance and induces fast moisture release. The above mentioned qualities make it viable to use this fabric for glove production for a wide range of purposes.
MicroSkin Shield®
MicroSkin Shield® is an exceptionally elastic fabric with good anti-friction capability, the core of which consists of an exceptionally strong, abrasion resistant, water repellent polyester yarn. Polyurethane coating of microstructure pattern guarantees flexibility and a perfect grip on various surfaces; it also improves resistance to water and grease.
Neoprene
Neoprene is synthetic chloroprene rubber. Neoprene is non-flammable and more durable than natural rubber and it is oil and solvent resistant. Neoprene features both good chemical stability and elasticity within a wide temperature range. This material contains millions of pores (air gaps) in which air is heated to human body temperature, thus it has good heat protective capabilities. The thicker is neoprene, the better the thermal protection feature. This material is often used for glove cuffs and production of cold and moisture resistant gloves.
Nitrile
Nitrile is a synthetic acrylonitrile and butadiene polymer. Nitrile gloves were developed as a solution for the growing group of people that are developing allergies to latex gloves. However, Nitrile has more advantages other than being made of synthetic rubber that is not an allergen. Another important feature of nitrile gloves is their durability. The nitrile glove is 3 times more puncture resistant than latex or a vinyl. After having improved production processes, the characteristics of nitrile gloves can be closely compared to their latex counterparts in terms of level of comfortability, elasticity (elongation limit 500%) and adaptability to hand shape. Nitrile gloves are widely used in machine repair shops and households where there is direct contact with lubricants, automotive petrol or other chemicals. Nitrile gloves are suitable to use at high temperatures, however they should be stored at low temperatures, in a dry and dark place. Nitrile is not as "sticky" as latex and the majority of people do not have problems when putting on and taking off the gloves. However nitrile is not as elastic as latex, therefore it is imperative to choose correct glove size.
Non-woven polypropylene
Non-woven polypropylene is non-woven fabric made of very thin plastic (polypropylene) fibres. Non-woven polypropylene is very practical fabric because it is very durable, soft, light-weight and cheap. Moreover, this fabric is easily recyclable after usage. It is most often used for surgical mask and gown production.
Nylon
Nylon is the trademarked name of polyamide fibre. This synthetic fibre is stretchy, durable and very resistant to wear and chemical reagents. It features better moisture absorption properties than other synthetic materials. Nylon is sensitive to sunlight and acquires a yellowish hue, thus it is often mixed with other fibres.
Polyamide
Polyamide is synthetic fibre that is extremely resistant to friction (about 10 times greater than cotton and 20 times more than wool). The polyamide fibre is very stretchy and static charge resistant. It is very light-weight, almost impermeable to water, non-creasing and durable. Polyamide is not flame-resistant and, moreover, melts when burning. Thus polyamide is often mixed with natural fibres increasing their durability and life time. Non rinsing products should be used for washing. The most popular type of polyamide is nylon.
Polyester
Polyester (PES) is a widely used synthetic heterochain polymer that is produced from petrol. This fibre is friction resistant, almost wrinkle-free, durable, and does not absorb moisture which expedites the drying process. Polyester is often mixed with wool, cotton or linen in order to increase durability, softness and glossiness, and reduce creasing of woven or knitted fabrics. Polyester products do not require special maintenance, however it should be noted that clothing with high polyester content should be kept away from heat and direct sunlight.
Polyethylene
PE - polyethylene is a thermoplastic, elastic and nontoxic polymer. It features high flame resistance and, once ignited, burns without soot. It is not soluble in any of the normal solvents at room temperature. It is chemically resistant to acids, alkalis, salt solutions and it is light-permeable. The main features of polyethylene are its density and melting index. When the density increases, the impact resistance and transparency decrease and there is a rise in melting temperature, density, strength, chemical resistance and impermeability to gas and odour. With the decrease of polyethylene melting index, its recyclability is impaired; however it features better resistance to impact, chemicals and wearing as well as having better sliding performance. In order to improve polyethylene characteristics, it has been modified in the following ways:
LDPELDPE - low density polyethylene (density 910 - 925 kg/m3) without extra polymerization. Such polyethylene is viscous and soft.
MDPEMDPE - medium density polyethylene (density 925 - 940 kg/m3) that combines the favoured characteristics of LDPE and HDPE.
HDPEHDPE - high density polyethylene (density 940 - 970 kg/m3). It is one of the most practical and cheapest materials and is very solid and durable but features less elasticity when compared to other polyethylenes.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP) is more durable and more temperature-resistant than polyethylene. Polypropylene density is one of the lowest (approx. 0.9 g/cm3) of all plastics. The maximum polypropylene usage temperature is 120-140°C. All polypropylene products can be sterilized repeatedly by vapor or boiling as this does not influence their shape or mechanical features. PP surpasses PE by its heat resistance features; however it is less cold resistant and becomes brittle at -5°C. Thus PP manufacturers add special additives to increase its resistance to low temperatures.
Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) is a thermoplastic elastomer. It is a very elastic material with good anti-friction characteristics. Glove palms coated with solid polyurethane are thin, straight and flexible. Glove palms coated with polyurethane microfoam are soft and water and lubricant resistant. Polyurethane microfoam is air permeable, therefore hands remain cool and dry. Polyurethane microfoam is rather flexible, it features great adhesion in dry environments.
ProTex® membrane
ProTex® membrane is polyurethane membrane that consists of numerous micropores that are smaller than a drop of water but bigger than a molecule of moisture vapor. Therefore, the membrane structure prevents water drops from entering, however sweat can easily evaporate out of the glove. The result of such a process is a non-permeable, wind resistant and "breathable" membrane.
PVC
PVC is polyvinyl chloride that is produced from oil and table salt. The PVC flexibility-rigidity scale is very wide, thus it can be extruded, rolled and sprayed. This is a very durable material that is resistant to acids, alkalis and alcohols. It can also acquire any desired color. This polymer with good chemical resistance features, low flammability class and good UV resistance is widely used in working glove production.
Spandex®
Spandex® is the name of elastomeric fibre (elastane) that is standardized in the USA. According to ISO standard this fibre is called elastane.
Typhoon®
Typhoon® is an extremely strong (yield strength) fibre combination characterised by the highest level of cut-resistance. Thanks to the applied technological solutions, the fibre combination consists of high molecular weight polyethylene, glass fibre and elastane. The yarn consisting of aforementioned fibres is elastic and characterised by air permeability and resistance to moisture. Typhoon® is light, 10 to 15 times stronger than steel (per unit weight) and up to 40% stronger than aramid fibres.
Vinyl
Vinyl is not as durable and elastic as latex or nitrile. It can be torn more easily, has an unpleasant odour and can be punctured easily. Vinyl is easier to obtain and is less expensive than latex and nitrile. Vinyl gloves do not fit snugly around the wrist, and they do not protect sufficiently against liquid penetration if the material is being stretched. Their low elasticity limits their comfortability and snug fitting on the hand. Vinyl does not contain natural rubber proteins or chemical accelerators and is therefore the most skin-friendly material available. Vinyl gloves are an economic choice for tasks that do not require high touch precision. Thus, vinyl is a perfect choice for low risk activities.
Water based polyurethane (PU)
Water based polyurethane (PU) is polyurethane without DMF (dimethylformamide) solvent and it is commonly used for the coating of gloves. Water based PU features more rapid degradation in the environment when compared to the traditional PU with DMF solvent.
